News

Time:2021-12-27
The American Diabetes Association (ADA), established in 1940, is a spontaneous health care organization in the United States that supports diabetes research and is engaged in diabetes information services. The "Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes" formulated by the ADA has been published since 1989 and has become one of the authoritative guidelines for instructing clinicians and nurses in the clinical practice of diabetes management. Recently, the ADA updated the guidelines based on the latest evidence-based evidence, and published the "2022 ADA Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes" in the Diabetes Care supplement. The standards of medical care continue to emphasize the concept of patient-centered. The management and treatment plan for diabetes has been improved.

The "2022 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes" divides the contents of Chapter 11 of the original 2021 version of the standards of medical care into two. Therefore, the 2022 version of the guidelines has been changed from the original 16 chapters to 17 chapters, including the following chapters:
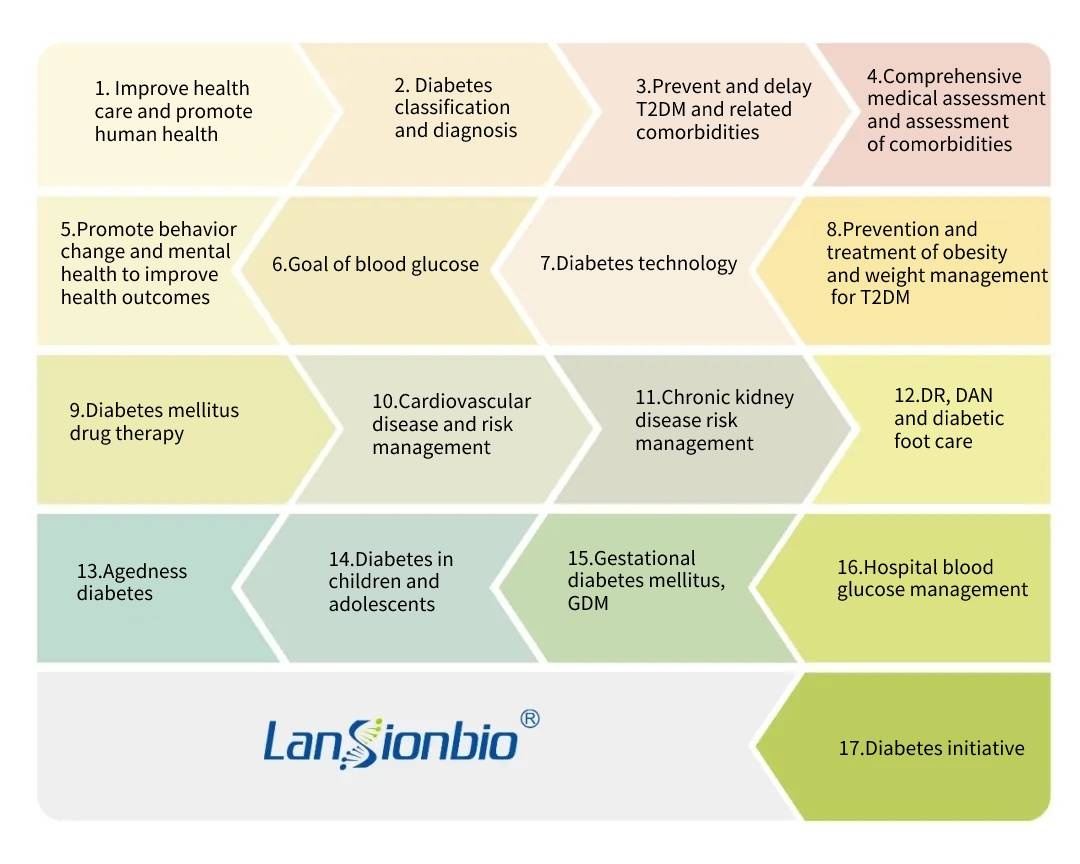
Diabetes is a complex chronic disease. Continuous diabetes self-management education and support are essential to prevent acute complications and reduce the risk of long-term complications. In diabetes health management, blood glucose monitoring is a very important part, but routine blood glucose testing has great volatility, which is related to the person’s diet, exercise and other factors on the day. Therefore, it is necessary to regularly test glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) as diagnose cut-point to understand the patient's condition changes and treatment effects, and provide a basis for adjusting diet and medication regimens. The 2022 ADA standard also emphasizes the connection between A1c and patient health management.
Patients who meet the treatment goals (and stable blood glucose control) should undergo blood glucose assessments (glycated hemoglobin (A1C) or other blood glucose indicators) at least twice a year. (E)
Patients who changes in the treatment plan and/or blood glucose levels that have not reached the target recently should be assessed for their blood glucose status at least quarterly. (E)
For many non-pregnant adult patients without significant hypoglycemia, an A1C target of <7% (53mmol/mol) is appropriate. (A)
Without causing obvious hypoglycemia or other side effects of treatment, according to the doctor's judgment and patient preference, lower A1C levels are acceptable. (B)
Patients who have a limited life expectancy or whose treatment does more harm than good may be suitable for a more relaxed A1C goal. (B)
Based on the criteria in the figure below, re-evaluate the blood glucose target over time. (E)
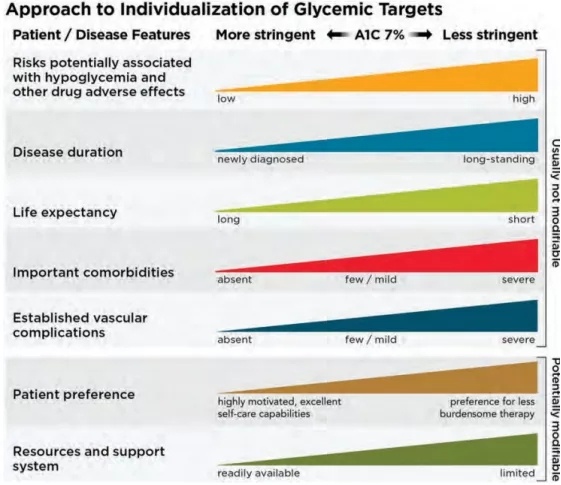
P1. Patients and disease factors that determine the best A1C goals
According to the conditions, preferences and treatment of diabetic patients, they are equipped with blood glucose monitoring equipment. Patients who use continuous blood glucose monitoring equipment must have blood glucose monitoring data available at all times. (A)
Patients who use insulin for blood glucose monitoring are encouraged to check blood glucose data at the right time based on the insulin regimen. For example, when fasting, before eating, before going to bed, before exercise, and when hypoglycemia is suspected, treat hypoglycemia until after the blood sugar is normal. Prior to key events such as driving, blood glucose monitoring should be used to assess blood glucose levels. (B)
For diabetic patients treated with multiple daily injections or continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion, when the device can be used safely, real-time continuous blood glucose monitoring (A) or intermittent scanning continuous blood glucose monitors should be used for diabetes management (B).
Diabetes patients undergoing basic insulin therapy can use real-time continuous blood glucose monitoring (A) or intermittent scanning continuous blood glucose monitors for diabetes management (C) when the equipment can be used safely.
For patients with multiple daily injections and continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion, real-time continuous blood glucose monitoring (CGM) equipment should be used every day as much as possible to get the greatest benefit. Intermittent scanning continuous blood glucose monitors should scan frequently, at least once every 8 hours. (A)
When used as an auxiliary means of pre- and post-prandial blood glucose monitoring, continuous blood glucose monitoring can help achieve the A1C goal of pregnant women with diabetes. (B)
Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) is the product of the combination of hemoglobin in red blood cells and sugars in serum through a non-enzymatic reaction. It has small biological variability, is not susceptible to blood sugar fluctuations, and does not require fasting or specific time for blood collection and analysis before analysis. The characteristics of low instability, etc., are not only a marker that reflects the blood sugar control status of diabetic patients, but also an effective indicator for evaluating blood sugar management treatment programs.
HbA1c is a biochemical test with strong convincing, objective data and good stability. It can not only reflect the glucose metabolism status of diabetic patients within 2 months, but also is closely related to diabetic complications, especially microangiopathy. International large-scale clinical trials such as DCCT and UKPDS have confirmed that the level of glycosylated hemoglobin in diabetic patients can be significantly reduced after intensive treatment, and the risk of various complications is also significantly reduced.
(1) Evaluate the long-term control level of diabetes, reflecting the patient's average blood glucose level during a period of 2 to 3 months before the blood test.
(2) It can be used as an indicator for monitoring the condition of diabetes, as well as an indicator for early diagnosis of mild, type II, and "hidden" diabetes.
(3) As a monitoring index to understand the patient's recent blood glucose status, and to evaluate the occurrence and development of chronic complications of diabetes.
(4) It is of great significance to prevent the occurrence and development of giant fetuses, malformed fetuses, stillbirths, and the occurrence and development of acute and chronic complications of diabetic pregnant women.
(5) For rescuers who are in a coma whose cause is not clear or are undergoing glucose infusion (the blood sugar is of course increased), urgent examination of glycosylated hemoglobin has the value of differential diagnosis.
(6)Diabetes patients with particularly increased HbA1c should be alert to the occurrence of acute comorbidities such as ketoacidosis.
Lansionbio Glycated Hemoglobin Test Kit adopts dry fluorescence immunochromatography technology and has obtained NGSP certification, marking that the test results of Lansionbio Glycated Hemoglobin can be traced to the internationally authoritative American Diabetes Control and Complications Clinical Research (DCCT) Reference method.

Equipped with a small immunoassay instrument, the results are accurate and the operation is convenient, and continuous blood glucose testing requirements can be completed at home. Massive data cloud transmission to terminal hospitals, tracking through telemedicine, comprehensive assessment and regular monitoring of the health status of diabetic patients, to optimize diabetes management, and improve the diagnosis and treatment plan, based on the joint decision-making and comprehensive evaluation of doctors and patients. Implement the "patient-centered" concept, proceed from actual needs and individual needs in clinical practice, and provide more accurate and comprehensive individualized diagnosis and treatment for diabetic patients.